NEW Story: Cocktail
Virgin Republic
| Virgin Republic | |
|---|---|
| Archipelago of the British, Spanish and U.S. Virgin Islands | |
| Constituent Republic of Vekllei | |
|
|
|
|
|
| Part of the Kalina Commonwealth | |
| Capital | Roadie (administrative) |
| Population | 282,295 |
| Area | 472.75 km² |
| Languages | English, French, Spanish |
| Vekllei Accession | 1836, as part of the British Atlantic Territories |
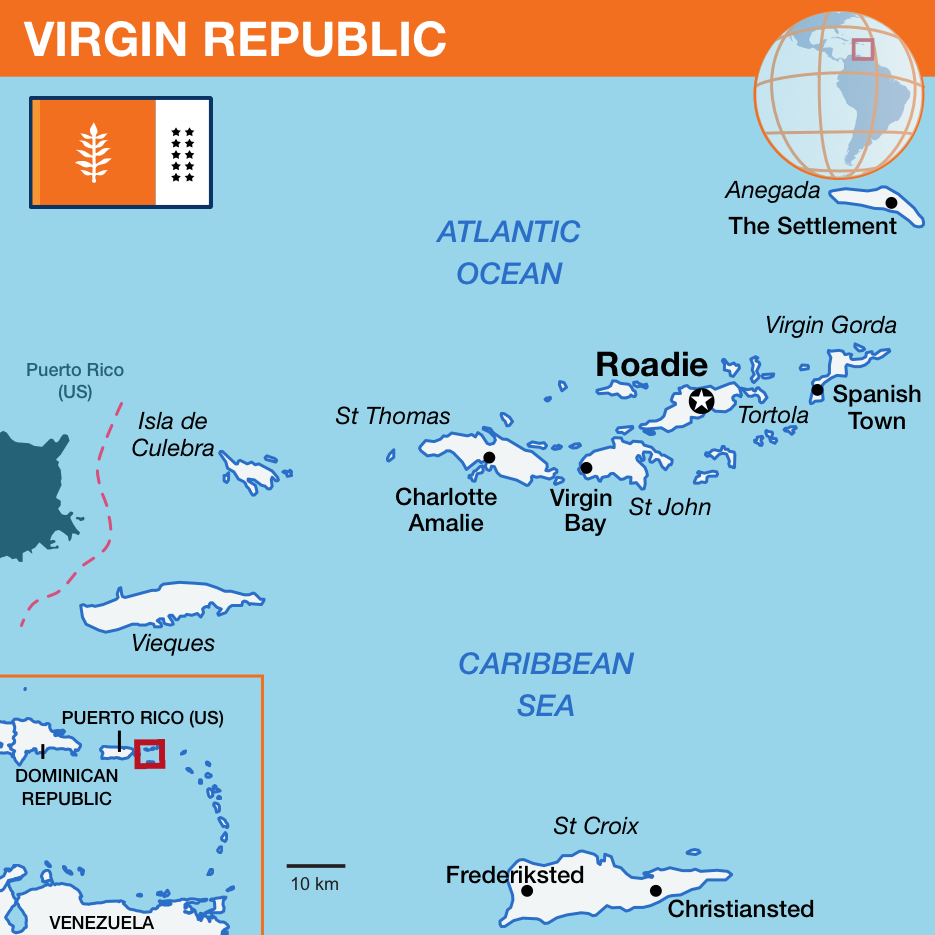
The Virgin Republic is a constituent republic of the Kalina Commonwealth in the Caribbean Sea, and is part of Vekllei. It is the westernmost part of the Kalina island group.
It comprises ten large islands in an archipelago extending eastwards of Puerto Rico (U.S.), as well as about 123 smaller islets and cays. Although these islands are situated on the fault-block mountains of the Puerto Rico trench, they are usually considered part of the Lesser Antilles due to their size and proximity of that chain. Virgin’s westernmost island, Vieques, forms the second-closest sea border to another country (Puerto Rico, part of the U.S.) after Kairi.
Before consolidation under the British Atlantic Territories, the Virgin archipelago was subject to competing colonial settlement and claims. English, Spanish, French and Danish ownership at various times contribute to the linguistic and cultural diversity within Virgin today. About three-quarters of its 182,000 people are black, descended from slaves who worked plantations in the colonial period. Substantial minority populations of Arawaks, Indians, Chinese and Europeans also exist. Protestant christianity is the majority religion.
Virgin’s climate is subtropical and pleasant, with warm weather cooled by trade winds crossing south. Individual islands are varied, often characterised by dense tropical forest that cover steep mountain interiors, and low-lying coastal plateaus that has been cleared for agriculture. Many natural harbours exist, many of which host major settlements including the capital of Roadie, and the cities of Charlotte Amalie and Christiansted.
Water scarcity across the islands has been historically severe, but alleviated in the 21st Century by desalination plants powered by nuclear fusion projects on the islands of St Croix and Tortola. The economy is dominated by the civil service, financial services and petrochemicals. Virgin refineries process oil from other parts of Vekllei for the Caribbean region. Virgin depends heavily on imports from other parts of the country, especially for machinery and manufactured goods.
Virgin University is the second-largest university in Kalina, and the fourth largest in Vekllei. It is common for students from smaller Commonwealth islands to travel to Virgin for study. The republic is also popular as a domestic holiday destination thanks to its excellent climate and world-renowned beaches.